Non Metals
As far as elements are concerned, a nonmetal is simply an element that does not display the properties of a metal. It is not defined by what it is, but by what it is not. It doesn’t look metallic, can’t be drawn into a wire or pounded into shape or bent, doesn’t conduct heat or electricity well, and doesn’t have a high melting or boiling point.
The nonmetals are in the minority on the periodic table, mostly pushed to the right hand side of the periodic table.
The exception is hydrogen, which behaves as a nonmetal at room temperature and pressure and is found on the upper left corner of the periodic table. Under conditions of high pressure, hydrogen is predicted to behave as an alkali metal.
Here’s a look at which elements are nonmetals, how to locate the nonmetals on the table, and their common properties.
LOCATION ON THE NONMETALS ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
The nonmetals are located on the upper right side of the periodic table. Nonmetals are separated from metals by a line that cuts diagonally through the region of the periodic table containing elements with partially filled p orbitals. 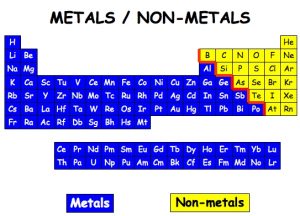 The halogens and noble gasesare nonmetals, but the nonmetal element group usually is considered to consist of the following elements:
The halogens and noble gasesare nonmetals, but the nonmetal element group usually is considered to consist of the following elements:
- hydrogen
- carbon
- nitrogen
- oxygen
- phosphorus
- sulfur
- selenium
The halogen elements are:
- fluorine
- chlorine
- bromine
- iodine
- astatine
- Possibly element 117 (tennessine), although most scientists think this element will behave as a metalloid.
The noble gas elements are:
- helium
- neon
- argon
- krypton
- xenon
- radon
- element 118 – oganesson (predicted to be a liquid, but still a nonmetal)
PROPERTIES OF NONMETALS
Nonmetals have high ionization energies and electronegativities. They are generally poor conductors of heat and electricity. Solid nonmetals are generally brittle, with little or no metallic luster.
Most nonmetals have the ability to gain electrons easily. Nonmetals display a wide range of chemical properties and reactivities.
SUMMARY OF COMMON PROPERTIES
- High ionization energies
- High electronegativities
- Poor thermal conductors
- Poor electrical conductors
- Brittle solids – not malleable or ductile
- Little or no metallic luster
- Gain electrons easily
- Dull, not metallic-shiny, although they may be colorful
- Lower melting points and boiling point than the metals
COMPARING THE METALS AND NONMETALS
Here’s a comparison of the physical and chemical properties of the metals and nonmetals. These properties apply to the metals in general (alkali metals, alkaline earth, transition metals, basic metals, lanthanides, actinides) and nonmetals in general (nonmetals, halogens, noble gases).
| Metals | Nonmetals | |
| chemical properties | easily lose valence electrons | easily share or gain valence electrons |
| 1-3 electrons (usually) in the outer shell | 4-8 electrons in the outer shell (7 for halogens and 8 for noble gases) | |
| form basic oxides | form acidic oxides | |
| good reducing agents | good oxidizing agents | |
| have low electronegativity | have higher electronegativity | |
| physical properties | solid at room temperature (except mercury) | may be liquid, solid, or gas (noble gases are gases) |
| have metallic luster | do not have metallic luster | |
| good conductor of heat and electricity | poor conductor of heat and electricity | |
| typically malleable and ductile | usually brittle | |
| opaque in a thin sheet | transparent in a thin sheet |