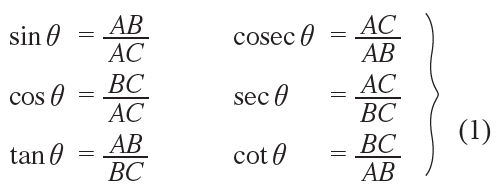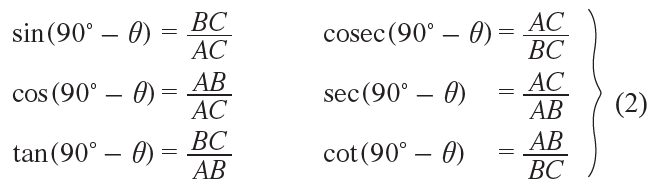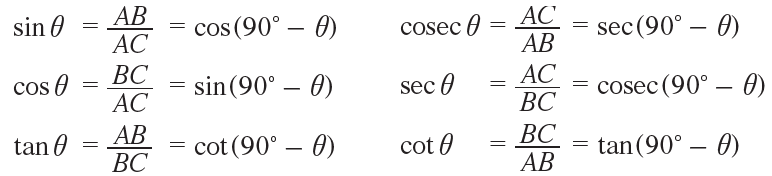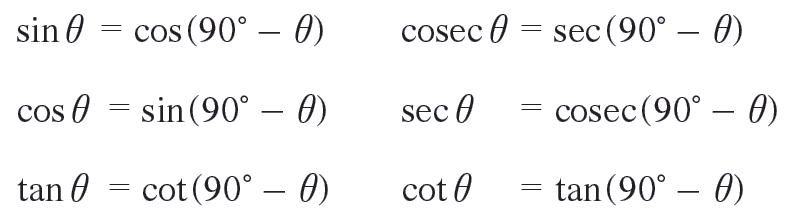Relation between arc radius and angle
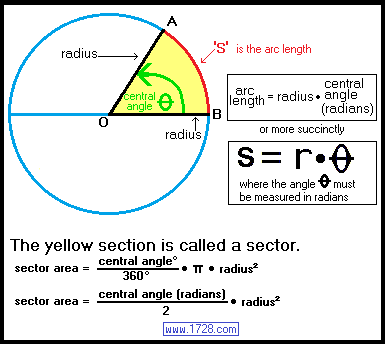
Arc length = [radius • central angle (radians)]
Arc length = circumference • [central angle (degrees) ÷ 360]
Proof of the trigonometric ratios of complementary allied angles
Two acute angles are complementary to each other if their sum is equal to 90°. In a right triangle the sum of the two acute angles is equal to 90°. So, the two acute angles of a right triangle are always complementary to each other.
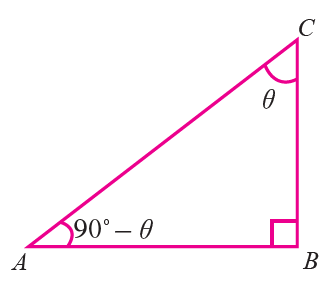
Let ABC be a right triangle, right angled at B
If <ACB = θ, then <BAC = 90° – θ and hence the angles <BAC and <ACB are complementary
For the angle θ, we have
Similarly, for the angle (90° – θ), we have
Comparing the equations in (1) and (2) we get,
Trigonometric Ratios of Complementary Angles
Examples: Evaluate : cos 56° /
sin 34°The angles 56° and 34° are complementary.
So, using trigonometric ratios of complementary angles, we have
cos 56° = cos (90° – 56°) = sin 34°
cos 56° / sin 34° = sin 34° / sin
34° = 1Hence the value of cos 56° / sin 34° is 1.
CGPCS Notes brings Prelims and Mains programs for CGPCS Prelims and CGPCS Mains Exam preparation. Various Programs initiated by CGPCS Notes are as follows:-